- 我们的平台 What is G2H
- 科学原理 The Science of Polygenic Scoring
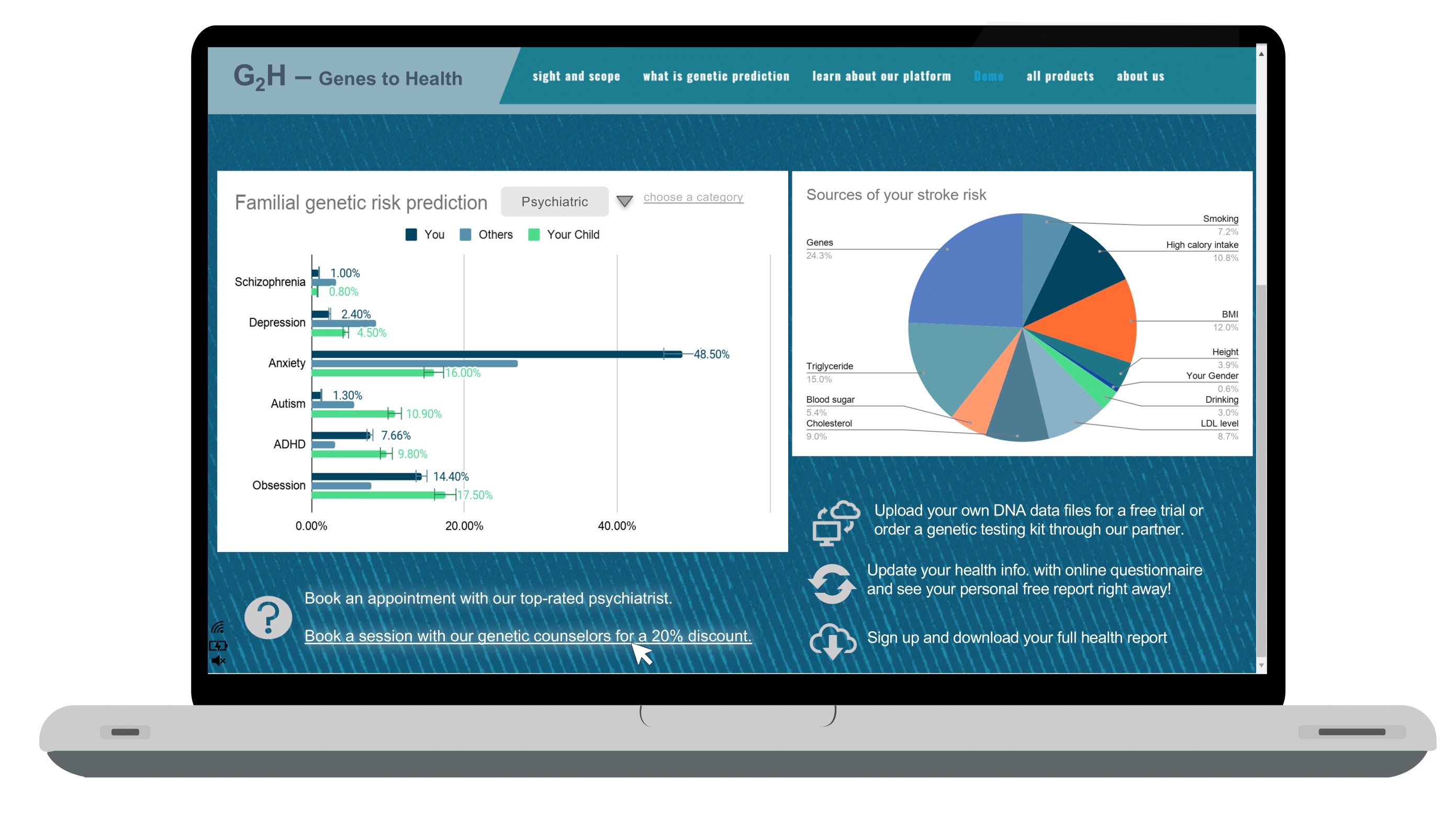
- 示例报告Sample Report
- 关于遗传检测 More about Genetic Testing
- 常见问题 FAQ
- 产品信息 Product Info
- 公司信息 Company Info
- 服务内容 All services
- 使用咨询 Consult before use
- 售后服务 Customer service
- 遗传咨询 Genetic counselling
- 临床咨询 Clinical counselling
- AI 虚拟咨询师 AI virtual counselling
- 近期活动 Recent activities
- 我们的平台 What is G2H
- 科学原理 The Science of Polygenic Scoring
- 示例报告Sample Report
- 关于遗传检测 More about Genetic Testing
- 常见问题 FAQ
- 产品信息 Product Info
- 公司信息 Company Info
- 服务内容 All services
- 使用咨询 Consult before use
- 售后服务 Customer service
- 遗传咨询 Genetic counselling
- 临床咨询 Clinical counselling
- AI 虚拟咨询师 AI virtual counselling
- 近期活动 Recent activities
Clinical Application of PRS
- 2025-02-09 02:34:00
- unfated 原创
- 1801
Polygenic Risk Scores (PRS) can be applied to clinical prediction, though there are both advantages and limitations to their use in a clinical setting.
How PRS Can Be Applied to Clinical Prediction:
-
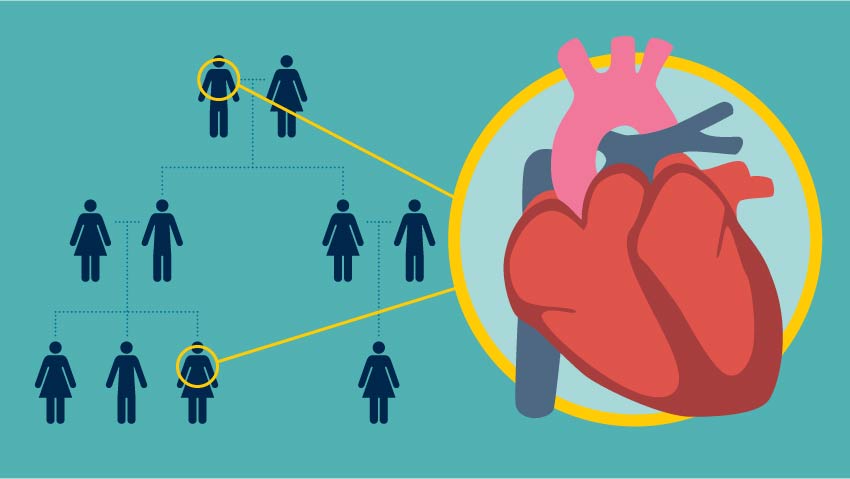
Risk Stratification: PRS can be used to classify individuals into different risk categories for developing certain diseases (e.g., heart disease, diabetes, certain cancers). For example, if a patient’s PRS indicates a high genetic risk for cardiovascular disease, clinicians might recommend more frequent screenings or preventive interventions such as lifestyle changes, medication, or other monitoring strategies.
-
Personalized Preventive Medicine: By combining genetic risk (from PRS) with environmental and lifestyle data, clinicians can tailor preventive measures more effectively. For example, an individual with a high PRS for type 2 diabetes could receive personalized advice on diet, exercise, and weight management to mitigate their genetic risk.
-
Early Detection: PRS could assist in identifying individuals at a higher genetic risk for diseases that have no early symptoms, like certain cancers or neurodegenerative conditions (e.g., Alzheimer’s). This could lead to earlier interventions, surveillance programs, or the use of predictive tests (like imaging) at an earlier stage.
-
Treatment Selection: In some cases, PRS could guide clinicians in choosing the most appropriate treatments based on an individual’s genetic predisposition. For example, some medications may work better for individuals with certain genetic backgrounds, so understanding their PRS can help optimize therapy.
Limitations in Clinical Application:
-
Polygenic Nature of Disease: PRS is based on the cumulative effect of many small genetic variants. This makes it more challenging to predict diseases accurately because each variant contributes only a small part of the overall risk. Many common diseases also involve complex interactions between genetics and environmental factors, making it difficult to isolate the contribution of genes alone.
-
Incomplete Prediction: PRS does not guarantee the onset of a disease. It only estimates the relative risk compared to the general population. For example, someone with a high PRS for heart disease may still never develop the condition due to protective lifestyle choices, while someone with a low PRS might still develop the disease due to other risk factors like diet or stress.
-
Genetic Data Interpretation: The accuracy of PRS depends on the quality and scope of the genetic data used to create the score. While large population studies have been instrumental in identifying genetic variants, there may be important genetic factors that haven't yet been discovered. Also, PRS models are typically developed for populations of European descent, and their applicability to individuals from other ethnic backgrounds may be limited.
-
Ethical and Psychological Concerns: The use of genetic information, including PRS, can raise ethical issues, such as the potential for genetic discrimination (in employment or insurance), privacy concerns, and psychological impacts (e.g., anxiety or stress from knowing one is at high risk for a disease). In clinical practice, care must be taken in how the information is communicated to patients.
-
Integration into Clinical Practice: While research on PRS has progressed rapidly, its widespread adoption into clinical practice still faces challenges. Clinical guidelines for using PRS are still being developed, and healthcare providers need more training on how to interpret and apply these scores.
Current and Future Applications:
-
Cardiovascular Diseases: PRS for cardiovascular risk is one of the most well-studied, and many studies suggest that it could be useful for identifying people at high risk for heart attacks or strokes. However, more evidence is needed on how to incorporate it into routine practice.
-
Cancer: For some cancers (e.g., breast cancer), PRS is showing promise in helping to identify individuals at higher risk, although current clinical guidelines don’t yet recommend it as part of routine screening.
-
Mental Health: PRS for psychiatric disorders (such as schizophrenia or depression) is an emerging area, but it is not yet ready for routine clinical use, as it faces significant challenges in terms of predictive power and how to integrate it with environmental and clinical factors.
In summary, while PRS holds significant potential for clinical prediction in areas like disease risk stratification, personalized medicine, and early detection, it’s not yet fully ready for widespread routine use in clinical practice. More research, improved accuracy, and better integration with other clinical data will be necessary for its full potential to be realized.
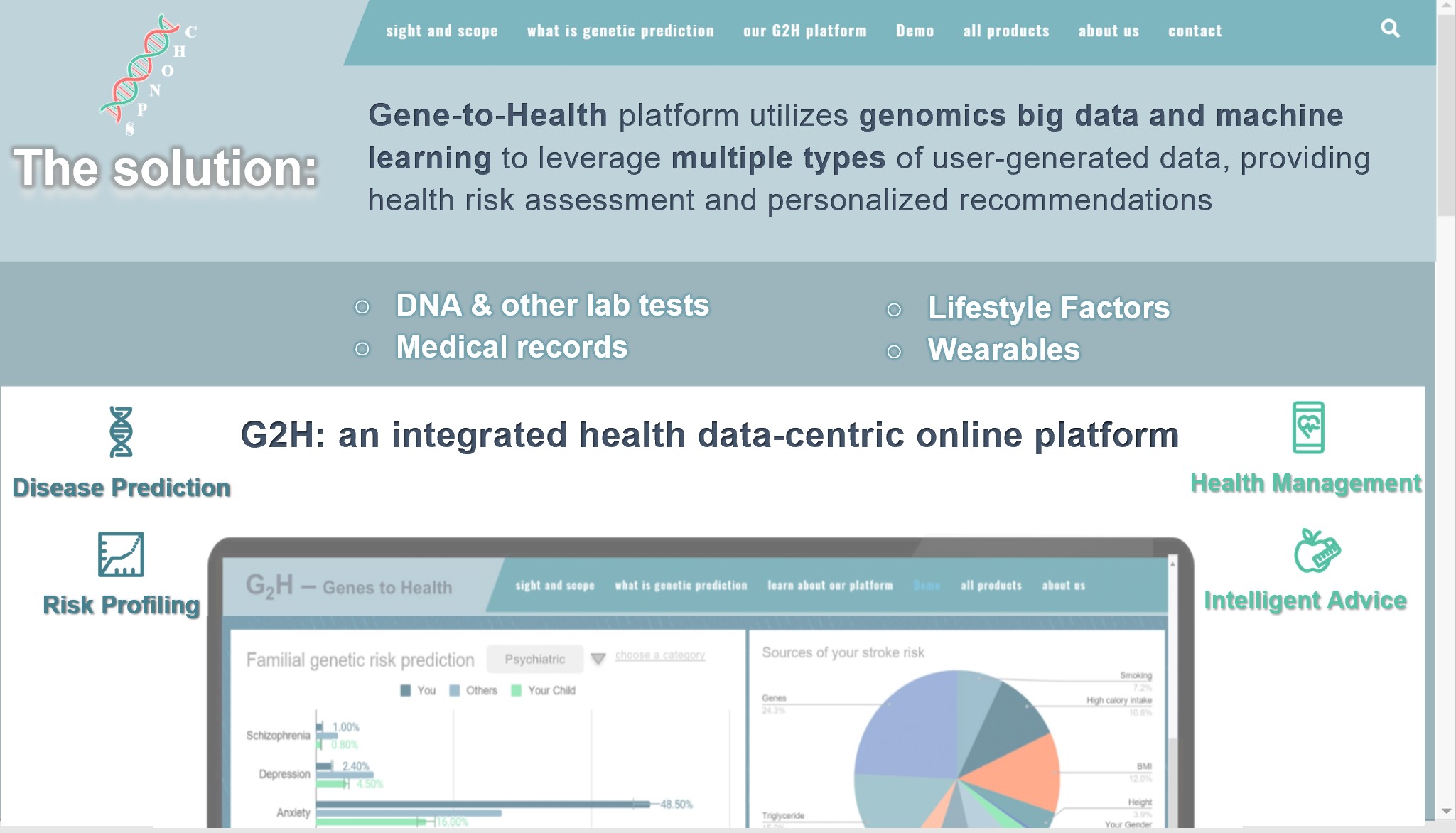
Gene to Health Limited primarily focuses on developing multi-omics predictive models for common disease risks, conducting biomedical big data analysis and modeling, and providing bioinformatics research services. We are a pioneer in Asia focused on polygenic scoring technology, leveraging millions of disease-related genetic variants and other omics data to predict over 1000 traits and diseases. Our core product suite, G2H, provides personalized health management solutions in one platform, including risk assessments for chronic diseases, dietary optimization, lifestyle advisory, and cancer risk prediction. We aim to revolutionize disease prevention and improve early disease intervention by integrating advanced genomic analysis, ML and AI.
我们是来自香港大学医学院 (HKU Med) 的博士创业团队,拥有以Polygenic Scoring (多基因风险评分,PGS)的核心技术,基因智健(G2H)平台是我们开发的核心产品。该平台主要利用基于多组学大数据的统计机器学习模型分析用户数据,从而预测和评估上千种种人类疾病风险和健康表型,为您的健康人生保驾护航。
| 联系人: | Dr. CHEN Guolan Lane |
|---|---|
| 电话: | +852 46404365 |
| Email: | support@gene2h.com |
| QQ: | 3028035047 |
| 微信: | lanechenhku |
| 微博: | u/7735987435 |
| 地址: | 1)Unit 707-34, 7F, Building 19W, No. 19 Science Park West Avenue, Hong Kong Science and Technology Park, Pak Shek Kok, N.T., Hong Kong 2)5 Sassoon Road, 1F, Pok Fu Lam, Hong Kong, China 3)Room 903, No. 91, Ke Feng Road, Huangpu District (Guangzhou Development Zone), Guangzhou, Guangdong Province, China 1)中国香港特别行政区新界白石角科技园西大道19号19W座7楼707-34单元 2)中国香港特别行政区薄扶林沙宣道5号1F 3)中国广东省广州市黄埔区(广州开发区)科丰路91号903 |
扫一扫企业微信客服,立即与我们沟通 (WeChat Customer Service)
Follow us at LinkedIn 关注领英