- 我们的平台 What is G2H
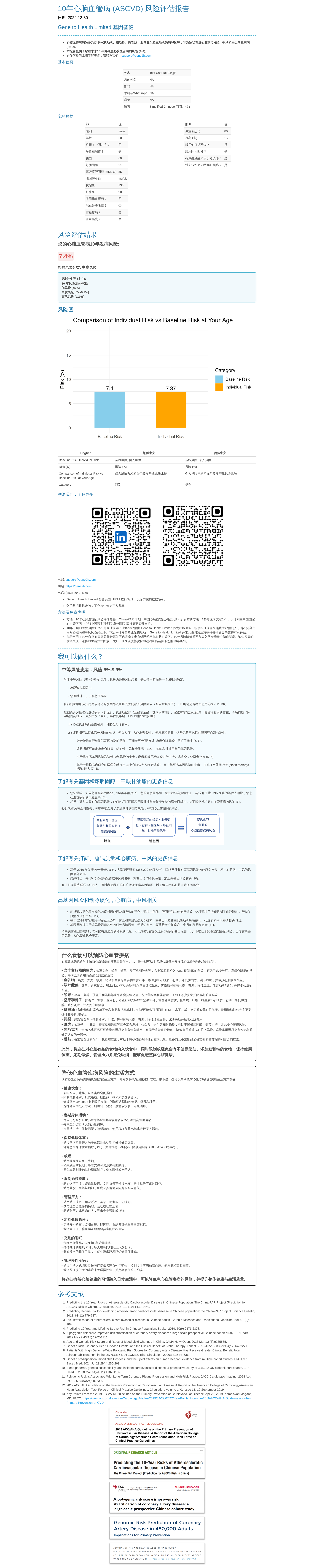
- 科学原理 The Science of Polygenic Scoring
- 示例报告Sample Report
- 关于遗传检测 More about Genetic Testing
- 常见问题 FAQ
- 产品信息 Product Info
- 公司信息 Company Info
- 服务内容 All services
- 使用咨询 Consult before use
- 售后服务 Customer service
- 遗传咨询 Genetic counselling
- 临床咨询 Clinical counselling
- AI 虚拟咨询师 AI virtual counselling
- 近期活动 Recent activities
PGS has great business value
- 2022-01-16 01:15:00
- Lane Chen
- 原创 11891
Scientific Background
For most common complex diseases, genetic risk cannot be attributed to only a single or several genes. Instead, numerous common variants have a contribution to the overall risk, each with a tiny effect. In fact, the number of such contributing variants usually ranges from 5,000 to 100,000, accounting for as many as 1% of all genomic common variants (Zhang et al. 2018). In other words, most complex diseases exhibit a highly polygenic architecture. These include psychiatric disorders, coronary artery disease, atrial fibrillation, inflammatory bowel disease, type 2 diabetes, Alzheimer, rheumatoid arthritis, obesity etc.
Consequently, screening high-risk individuals by focusing on rare monogenic mutations of a handful of previously reported high-risk genes only benefits a small proportion of the population who are carriers. Unless we adopt a polygenic scoring approach, most people would miss out on the benefits of genetic risk assessment.
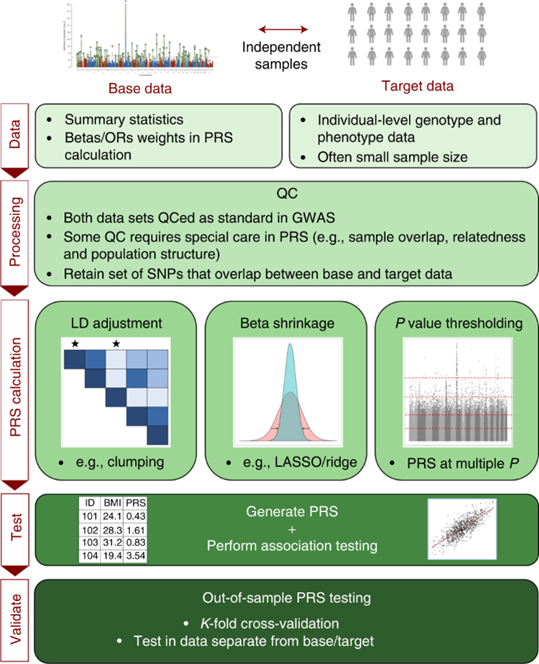
Polygenic scoring is a technique of statistical estimation that evaluates the overall genetic risk by assigning a tiny weight to each variant’s genotype and aggregating them to a genome-wide sum score. Initially, its realization can be very simple (clumping plus thresholding), but now the mainstream modelling includes some complicated penalized regression or Bayesian approaches. The training of PGS relies on a base dataset that is the summary statistics of one large GWAS on our interested phenotype, and another target dataset with individual-level genotype and phenotype is usually needed for hyperparameter optimization and performance evaluation.
Main Benefits
The major utility of polygenic scoring is to predict an individual’s risk for all kinds of complex diseases. They inform us about an individual’s relative risk compared to the remainder of the population, and can bring many additional benefits.
Polygenic scoring is applicable at any scale of genotype data, whether array genotyping, exome sequencing or whole genome sequencing, with varying accuracy.
Polygenic scoring gives physicians new tools for diagnosis and treatment.
It helps to stratify patient population according to risk and identify individuals who would most benefit from additional monitoring or early preventative measures to offset the risk of disease.
It would greatly improve the scale that a genetic testing report can cover and tremendously enrich the contents delivered to consumers. Curated pretrained PGSs in this catalog have covered 219 traits. If we use famous publicly-available large cohorts (UK Biobank, Japan Biobank, FinnGen) for training, much more could be covered. For example, the UK Biobank comprises over 600 diseases and over 2,800 other traits. As a comparison, CircleDNA currently appears to cover around 120 common diseases and 160 rare mendelian disorders.
By combining with environmental factors or clinical factors, PRS provide more accurate risk assessment and stratification, demonstrating a way to make personalized lifestyle recommendations based on an individual’s genetic profile. It also strengthens users’ motivation and willingness to provide personal environmental or clinical information, which they see as beneficial to their own health prediction.
Potential Value
Both individual consumers of genetic testing service and clinicians can benefit from polygenic scoring. It provides 5~10 times more information for the users than traditional monogenic approach, although in general its accuracy is still insufficient for clinical-level use. However, most clients, as layman in genetics, are more concerned about whether they have high risks for all kinds of common severe diseases, other than the exact odds ratio, relative risks or effect size. Particularly, polygenic scoring greatly broadens the scope of cancer risk prediction by covering over 100 types of cancers. Even though high cancer PGSs are far from being regarded as diagnostic evidence, they still give the clients a suggestion about on what types of cancers they should go ahead for clinical-level cancer screening tests. Noteworthily, for several diseases like coronary artery disease, PGS succeeds in identifying individuals with risk equivalent to monogenic mutations (Khera et al., 2018). Besides, research in the past decade show that polygenic scoring might be the best way to identify people with high risks of psychiatric disorders such as depression, autism, ADHD and schizophrenia, which are extremely polygenic, highly inheritable and lacking in biological useful and valid biomarkers, making another selling point to parents of children and teenagers.
We also see insurance companies like Swiss Re. and Hannover Re. show interest in incorporating polygenic scoring into health insurance services. Undoubtedly, it is promising that polygenic scoring could add great value to profitability of DTC genetic testing service.
On top of that, we see much greater potential value beyond financial gain.
Polygenic scoring is at the cutting edge of genomic medicine research. It is a very hot topic with many papers receiving hundreds to thousands of citations. Research institutions in some leading areas, like Harvard-MIT Broad Institute, Oxford University and Stanford University, have already been applying for relevant patents (e.g. US 2021/0065846 A1) and translating these advances into businesses. For example, Allelica Inc., a company with valuation around 10 million USD, is aiming to provide cardiovascular disease polygenic scoring directly to consumers and is backed by famous research groups. Being the first in Asia to incorporate polygenic scoring explicitly to the service would add much to Prenetics’s brand value by demonstrating its innovation capacity to the media. We believe that
Polygenic scoring is a complex statistical methodology that requires PhD-level expertise and sophistication in modelling. Building up a cooperative team for specialized PGS bioinformatic analysis service will also bring advantage in getting Prenetics a participating role in emerging large biobank projects all around Asia, like the Hong Kong Genome Project that plans to perform whole-genome sequencing on 50,000 subjects. The availability of local population data from such large cohort would also address the current challenge of cross-ancestry application.
Further, PRS is big-data based, which means that accumulation of users’ data tends to improve the prediction accuracy. Therefore, the earlier to launch the PRS analysis module, the better results we can obtain in the future. There is a great opportunity cost to risk losing the “first mover advantage” to competitors.Gene to Health Limited primarily focuses on developing multi-omics predictive models for common disease risks, conducting biomedical big data analysis and modeling, and providing bioinformatics research services. We are a pioneer in Asia focused on polygenic scoring technology, leveraging millions of disease-related genetic variants and other omics data to predict over 1000 traits and diseases. Our core product suite, G2H, provides personalized health management solutions in one platform, including risk assessments for chronic diseases, dietary optimization, lifestyle advisory, and cancer risk prediction. We aim to revolutionize disease prevention and improve early disease intervention by integrating advanced genomic analysis, ML and AI.
我们是来自香港大学医学院 (HKU Med) 的博士创业团队,拥有以Polygenic Scoring (多基因风险评分,PGS)的核心技术,基因智健(G2H)平台是我们开发的核心产品。该平台主要利用基于多组学大数据的统计机器学习模型分析用户数据,从而预测和评估上千种种人类疾病风险和健康表型,为您的健康人生保驾护航。
| 聯繫人: | Dr. CHEN Guolan Lane |
|---|---|
| 電話: | +852 46404365 |
| Email: | support@gene2h.com |
| QQ: | 3028035047 |
| 微信: | lanechenhku |
| 微博: | u/7735987435 |
| 地址: | 1)Unit 707-34, 7F, Building 19W, No. 19 Science Park West Avenue, Hong Kong Science and Technology Park, Pak Shek Kok, N.T., Hong Kong 2)5 Sassoon Road, 1F, Pok Fu Lam, Hong Kong, China 3)Room 903, No. 91, Ke Feng Road, Huangpu District (Guangzhou Development Zone), Guangzhou, Guangdong Province, China 1)中国香港特别行政区新界白石角科技园西大道19号19W座7楼707-34单元 2)中国香港特别行政区薄扶林沙宣道5号1F 3)中国广东省广州市黄埔区(广州开发区)科丰路91号903 |
扫一扫企业微信客服,立即与我们沟通 (WeChat Customer Service)
Follow us at LinkedIn 关注领英