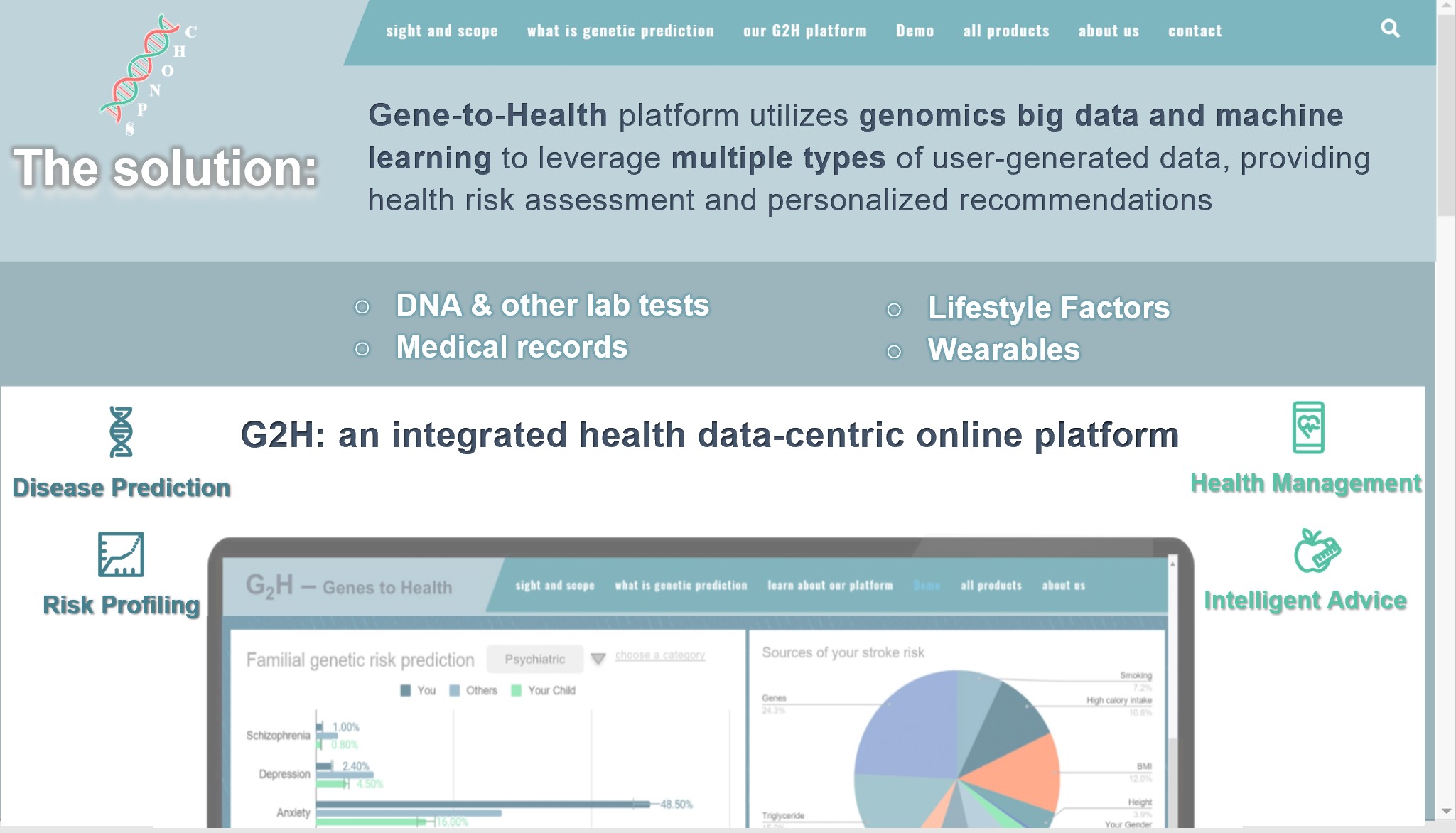
- 我们的平台 What is G2H
- 科学原理 The Science of Polygenic Scoring
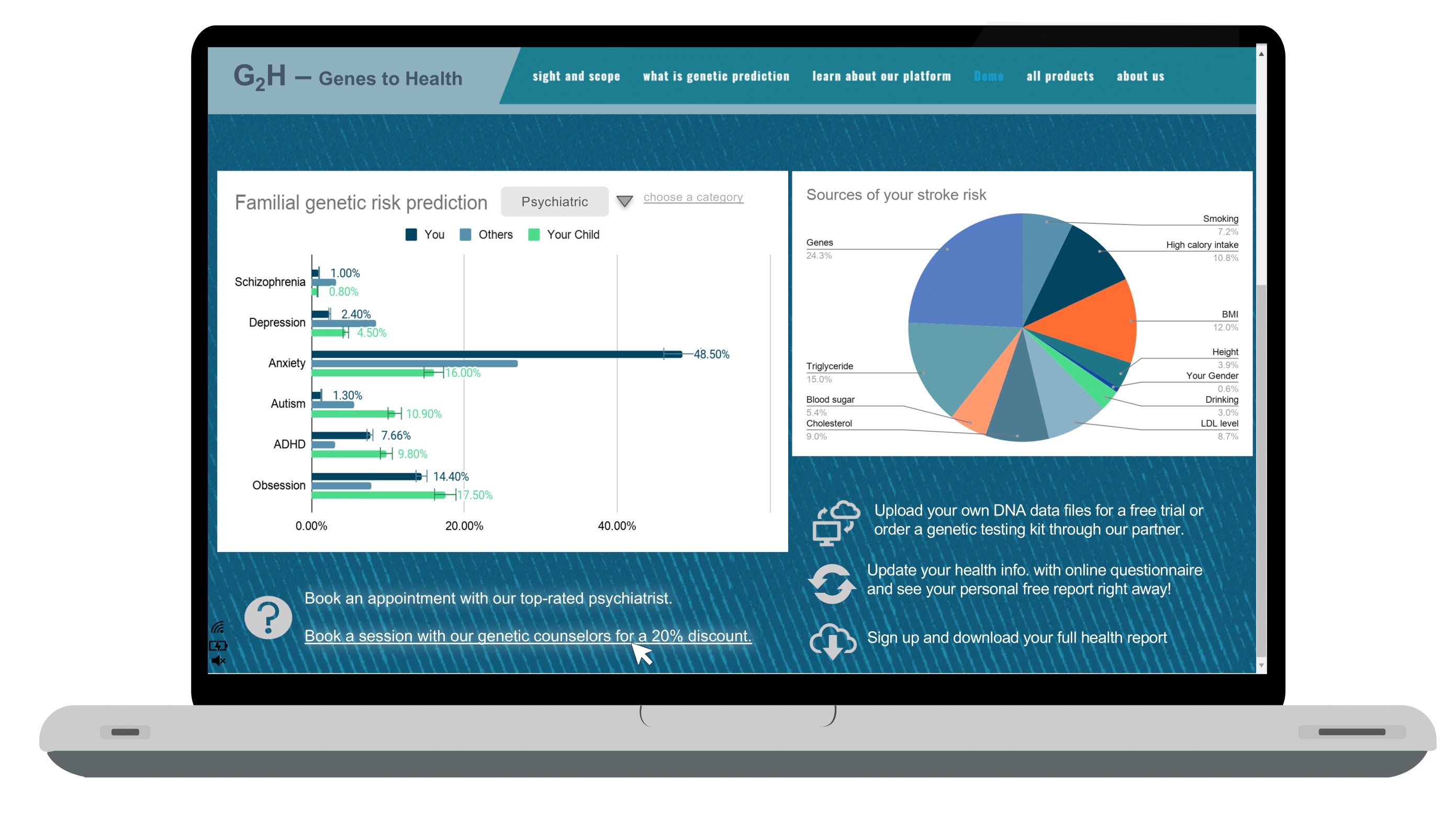
- 示例报告Sample Report
- 关于遗传检测 More about Genetic Testing
- 常见问题 FAQ
- 产品信息 Product Info
- 公司信息 Company Info
- 服务内容 All services
- 使用咨询 Consult before use
- 售后服务 Customer service
- 遗传咨询 Genetic counselling
- 临床咨询 Clinical counselling
- AI 虚拟咨询师 AI virtual counselling
- 近期活动 Recent activities
- 我们的平台 What is G2H
- 科学原理 The Science of Polygenic Scoring
- 示例报告Sample Report
- 关于遗传检测 More about Genetic Testing
- 常见问题 FAQ
- 产品信息 Product Info
- 公司信息 Company Info
- 服务内容 All services
- 使用咨询 Consult before use
- 售后服务 Customer service
- 遗传咨询 Genetic counselling
- 临床咨询 Clinical counselling
- AI 虚拟咨询师 AI virtual counselling
- 近期活动 Recent activities
G2H Scope of Services and Quotation
- 2025-02-05 11:20:00
- unfated 原创
- 1186
Scope of Services and Quotation
Introduction
Gene to Health Limited is pleased to present our comprehensive Scope of Services and Quotation tailored to support your research laboratory's data analysis and omics research needs. Leveraging our expertise in advanced genetic and bioinformatics analyses, we are committed to delivering PhD-level, high-quality, cost-effective solutions to enhance your research capabilities.
Quotation
All base prices are in Hong Kong Dollars (HKD) and are subject to uprise change based on project scope and specific requirements.
|
Service |
Description |
Base Price (HKD) Per Project |
|
Bioinformatic Services |
|
|
|
1. GWAS-based Statistical Genetic Analysis |
Comprehensive array genetic data analysis using multiple tools |
$10,000 |
|
2. Single-Cell Omics Analysis |
Detailed single-cell genomic and transcriptomic analysis |
$20,000 |
|
3. Polygenic Risk Score (PRS) Development |
PRS training, modeling, and validation |
$8,000 |
|
4. Epidemiological Statistical Models |
Implementation of Cox and other statistical models |
$5,000 |
|
5. Supervised Machine Learning Models |
Development and evaluation of ML models on biomedical data |
$3,000 |
|
6. Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) Analysis |
Comprehensive NGS data analysis |
$20,000 |
|
7. Long Read Sequencing Analysis |
Analysis of long-read sequencing data |
$25,000 |
|
8. Post-GWAS Analyses |
Comprehensive post-GWAS analysis services |
$15,000 |
|
9. Mendelian Randomization |
Mendelian Randomization analysis to infer causal relationships |
$8,000 |
|
10. Metagenomic Data Analysis |
Taxonomic and functional profiling of metagenomic data |
$15,000 |
|
11. Multi-Omics Data Integration |
Integrating various omics data for comprehensive analysis |
$10,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
General Services |
|
|
|
1. AWS Cloud Services Setup |
Development of cloud-based data management and report systems |
$30,000 |
|
2. English Manuscript Editing and Polishing |
Professional editing services for scientific manuscripts |
$3,000 per manuscript |
|
3. R and Python Data Visualization and Figure Composition |
Creation of custom data visualizations |
$2,000 per figure |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Additional Services |
|
|
|
a. Data Visualization Dashboards |
Development of interactive dashboards |
$8,000 |
|
b. Bioinformatics Consulting |
Strategic planning and custom pipeline development |
$6,000 per session |
|
c. Technical Support and Training |
User training and ongoing technical support |
$5,000 per month |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total Estimated Cost: Varies based on selected services
Special Package Offer: For clients opting for multiple (>3) services, a 10% discount is applicable.
Terms and Conditions
- Payment Terms: 30% upfront upon agreement, 70% upon project completion. Or by milestones upon negotiations. All payments shall be settled within 30 days against invoice date.
- Delivery Timeframe: Dependent on project scope; estimated between 2-12 weeks.
- Revisions: Includes up to two rounds of major revisions and five rounds of minor revisions per deliverable.
- Confidentiality: All client data will be handled with strict confidentiality.
- Validity: Quotation valid for 30 days from the date of issuance.
- Deliverability: All analyzed data, software outputs, pipeline instructions and deliverable results (such as figures, tables, trained models, parameters) will be returned to clients. The availability of generated scripts is negotiable, depending on contract scope, client’s demands, and involvement of key intellectual properties.
Scope of Services
Bioinformatic Services
1. GWAS-based Statistical Genetic Analysis
Description: Comprehensive genome-wide association analyses (GWAS) of genetic data to identify associations between genetic variants and various phenotypic traits.
Tools & Software:
- Primary: PLINK, REGENIE, GCTA, GATK
- Additional: LDSC, FUMA, BOLT-LMM, EIGENSOFT, SNPTEST, EMMAX, METAL, FINEMAP
Pipeline & Processes:
- Data Cleaning & Quality Control: Ensuring data integrity by removing low-quality samples and variants.
- Population Stratification: Correcting for population structure using principal component analysis (PCA).
- Genome-Wide Association Studies (GWAS): Identifying significant genetic variants associated with specific traits.
- Heritability Estimation: Calculating the proportion of variance explained by genetic factors.
- Imputation: Enhancing genotype data completeness using reference panels.
- Meta-Analysis: Combining results from multiple studies to increase statistical power.
2. Single-Cell Omics Analysis
Description: Detailed analysis of single-cell genomic and transcriptomic data to understand cellular heterogeneity and complex biological processes.
Tools & Software:
- Primary: Partek Flow
- Additional: Seurat, Scanpy, CellRanger, Monocle, Drop-seq Tools, SingleR
Pipeline & Processes:
- Data Preprocessing: Quality control, normalization, and scaling of single-cell data.
- Clustering & Dimensionality Reduction: Identifying distinct cell populations using PCA, t-SNE, or UMAP.
- Differential Expression Analysis: Detecting genes with significant expression changes across clusters.
- Trajectory Analysis: Inferring cellular development pathways and lineage relationships.
- Integration of Multi-Modal Data: Combining single-cell RNA-seq with other data types (e.g., ATAC-seq).
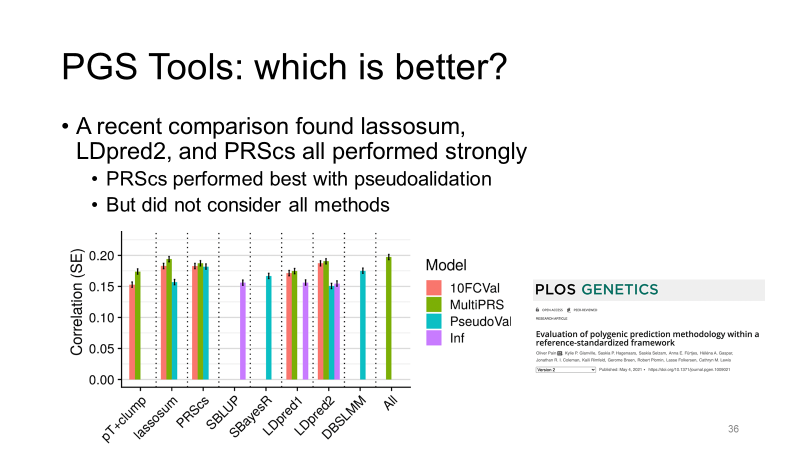
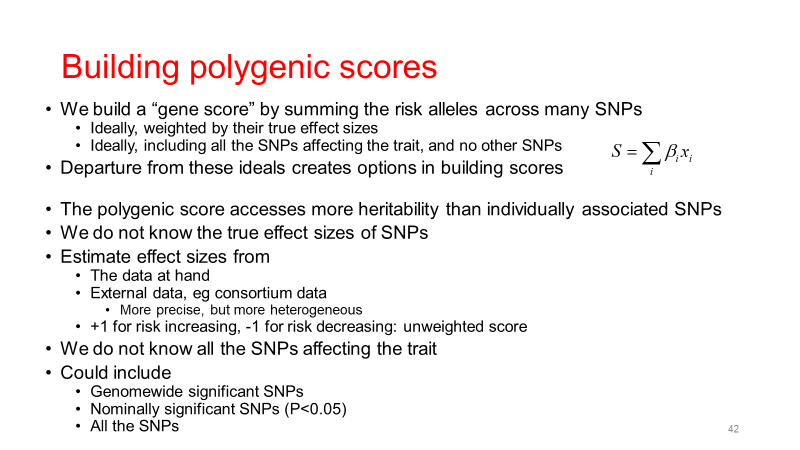
3. Polygenic Risk Score (PRS) Training, Modeling, and Testing
Description: Development and validation of polygenic risk scores to predict individual susceptibility to various health conditions based on genetic data.
Tools & Software:
- Primary: PRSice, LDpred, PRS-CS
- Additional: PLINK, LASSOSUM, SBayesR
Pipeline & Processes:
- SNP Selection: Identifying relevant genetic variants for the risk score.
- Weighting: Assigning effect sizes to each SNP based on GWAS results.
- Score Calculation: Aggregating weighted SNPs to compute individual PRS.
- Validation: Testing the predictive accuracy of PRS in independent cohorts.
- Optimization: Refining models to improve prediction performance.
4. Epidemiological Statistical Models
Description: Application of statistical models to study the distribution and determinants of health-related states and events within populations.
Tools & Software:
- Primary: R (e.g. survival package)
- Additional: Python (e.g. statsmodels)
Pipeline & Processes:
- Cox Proportional Hazards Models: Assessing the impact of variables on time-to-event outcomes.
- Logistic Regression: Modeling binary outcomes.
- Linear Regression: Analyzing continuous traits.
- Mixed-Effects Models: Handling hierarchical or longitudinal data structures.
- Survival Analysis: Estimating survival functions and hazard ratios.
5. Supervised Machine Learning Models
Description: Implementation of machine learning techniques to predict outcomes and identify patterns within your data.
Tools & Software:
- Primary: Scikit-learn (Python), Random Forest, Support Vector Machines (SVM), Neural Networks
- Additional:
- Boosting Algorithms: XGBoost, LightGBM, AdaBoost, CatBoost
- Deep Learning Frameworks: PyTorch
- Ensemble Methods: Gradient Boosting Machines (GBM), Extra Trees, Bagging
- Regression Models: ElasticNet, Lasso, Ridge Regression
- Other Algorithms: Naive Bayes, Decision Trees
Pipeline & Processes:
- Data Preparation: Feature selection, engineering, and data splitting into training and testing sets.
- Model Training: Building models using algorithms like Random Forest, SVM, Gradient Boosting, and Neural Networks.
- Model Evaluation: Assessing performance using metrics such as accuracy, precision, recall, F1-score, and AUC-ROC.
- Hyperparameter Tuning: Optimizing model parameters for improved performance.
- Model Deployment: Integrating models into existing workflows or systems.
6. Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) Analysis
Description: Comprehensive analysis of next-generation sequencing (NGS) data to provide insights into genomic, transcriptomic, and epigenomic landscapes.
Tools & Software:
- Primary: Illumina BaseSpace, Bowtie2, STAR, HISAT2
- Additional: BWA, SAMtools, BEDTools, DESeq2, EdgeR, FastQC, MultiQC
Pipeline & Processes:
- Quality Control: Assessing sequencing quality using FastQC and MultiQC.
- Read Alignment: Mapping reads to reference genomes using BWA, Bowtie2, or STAR.
- Variant Calling: Identifying SNPs and indels with tools like GATK and SAMtools.
- Transcriptome Assembly: Assembling RNA-seq data using HISAT2 and StringTie.
- Differential Expression Analysis: Utilizing DESeq2 and EdgeR for identifying differentially expressed genes.
- Functional Annotation: Annotating variants and genes using ANNOVAR and SnpEff.
- Data Integration: Combining NGS data with other omics datasets for multi-dimensional analysis.
7. Long Read Sequencing Analysis
Description: Advanced analysis of long-read sequencing data to resolve complex genomic regions, detect structural variants, and enhance genome assemblies.
Tools & Software:
- Primary: SMRT Analysis (PacBio), Nanopore Tools (ONT)
- Additional: Canu, Flye, Minimap2, Longshot, Porechop, Guppy, Racon, Pilon, SVIM, Sniffles, Prokka, MAKER
Pipeline & Processes:
- Basecalling: Converting raw sequencing data into nucleotide sequences using Guppy or similar tools.
- Read Filtering: Removing low-quality reads and adapters with Porechop and Fastp.
- Alignment: Mapping reads to reference genomes using Minimap2 or BWA-MEM.
- De Novo Assembly: Constructing genome assemblies from long reads with Canu or Flye.
- Hybrid Assembly: Combining long reads with short reads for improved assembly accuracy.
- Error Correction: Refining assemblies using Racon for consensus polishing and Pilon for further error correction.
- Structural Variant Detection: Identifying large insertions, deletions, inversions, and translocations using tools like SVIM and Sniffles.
- Annotation: Annotating assembled genomes with functional and structural information using Prokka and MAKER.
- Comparative Genomics: Comparing assemblies across different samples or conditions to identify genomic variations.
8. Post-GWAS Analyses
Description: Post-GWAS analyses help interpret genetic associations identified in Genome-Wide Association Studies (GWAS), linking statistical results to biological mechanisms. They pinpoint causal variants, explore genetic architectures, and assess functional impacts.
Key Analyses:
- Fine-Mapping
- Objective: Identify likely causal variants in associated loci.
- Tools: CAVIAR, FINEMAP
- Process: Integrate GWAS statistics with LD data, perform statistical fine-mapping, prioritize variants for validation.
- Functional Annotation
- Objective: Understand the biological functions of variants and their impact on gene regulation or protein function.
- Tools: ANNOVAR, VEP
- Process: Annotate variants with genomic locations, regulatory elements, and gene associations.
- Pathway Enrichment
- Objective: Identify biological pathways enriched with associated genes.
- Tools: MAGMA, DAVID
- Process: Map variants to genes, perform enrichment analysis, interpret relevant pathways.
- Colocalization Analysis
- Objective: Assess if the same variant affects multiple traits.
- Tools: COLOC, SMR
- Process: Integrate GWAS with eQTL data, test shared genetic architecture.
- Gene-Based Testing
- Objective: Evaluate the cumulative effect of gene variants on traits.
- Tools: MAGMA, VEGAS2
- Process: Aggregate variant associations within genes, perform statistical tests.
- Heritability Partitioning
- Objective: Estimate contributions of functional categories to trait heritability.
- Tools: LDSC
- Process: Assign SNPs to functional categories and estimate their heritability.
- eQTL Analysis
- Objective: Link GWAS variants with gene expression.
- Tools: GTEx, FastQTL
- Process: Cross-reference GWAS variants with eQTL databases, explore gene regulation mechanisms.
9. Mendelian Randomization Study
Description: Mendelian Randomization (MR) uses genetic variants as instrumental variables to infer causal links between risk factors and health outcomes, reducing confounding and reverse causality.
Tools & Software:
- Primary: MRBase, MVMR, TwoSampleMR, MRInstruments
- Additional: GCTA, PLINK
Pipelines & Processes:
- Instrumental Variables Selection
- Objective: Identify SNPs st
Gene to Health Limited primarily focuses on developing multi-omics predictive models for common disease risks, conducting biomedical big data analysis and modeling, and providing bioinformatics research services. We are a pioneer in Asia focused on polygenic scoring technology, leveraging millions of disease-related genetic variants and other omics data to predict over 1000 traits and diseases. Our core product suite, G2H, provides personalized health management solutions in one platform, including risk assessments for chronic diseases, dietary optimization, lifestyle advisory, and cancer risk prediction. We aim to revolutionize disease prevention and improve early disease intervention by integrating advanced genomic analysis, ML and AI.
我们是来自香港大学医学院 (HKU Med) 的博士创业团队,拥有以Polygenic Scoring (多基因风险评分,PGS)的核心技术,基因智健(G2H)平台是我们开发的核心产品。该平台主要利用基于多组学大数据的统计机器学习模型分析用户数据,从而预测和评估上千种种人类疾病风险和健康表型,为您的健康人生保驾护航。
| 联系人: | Dr. CHEN Guolan Lane |
|---|---|
| 电话: | +852 46404365 |
| Email: | support@gene2h.com |
| QQ: | 3028035047 |
| 微信: | lanechenhku |
| 微博: | u/7735987435 |
| 地址: | 1)Unit 707-34, 7F, Building 19W, No. 19 Science Park West Avenue, Hong Kong Science and Technology Park, Pak Shek Kok, N.T., Hong Kong 2)5 Sassoon Road, 1F, Pok Fu Lam, Hong Kong, China 3)Room 903, No. 91, Ke Feng Road, Huangpu District (Guangzhou Development Zone), Guangzhou, Guangdong Province, China 1)中国香港特别行政区新界白石角科技园西大道19号19W座7楼707-34单元 2)中国香港特别行政区薄扶林沙宣道5号1F 3)中国广东省广州市黄埔区(广州开发区)科丰路91号903 |
扫一扫企业微信客服,立即与我们沟通 (WeChat Customer Service)
Follow us at LinkedIn 关注领英